Harnessing Insights with Looker Studio's Waterfall Charts
Advantages of Waterfall Charts for Data Visualization:
Clutter Avoidance in Waterfall Charts:
Types and Categories of Waterfall Charts in Looker Studios:
1. Waterfall Chart:
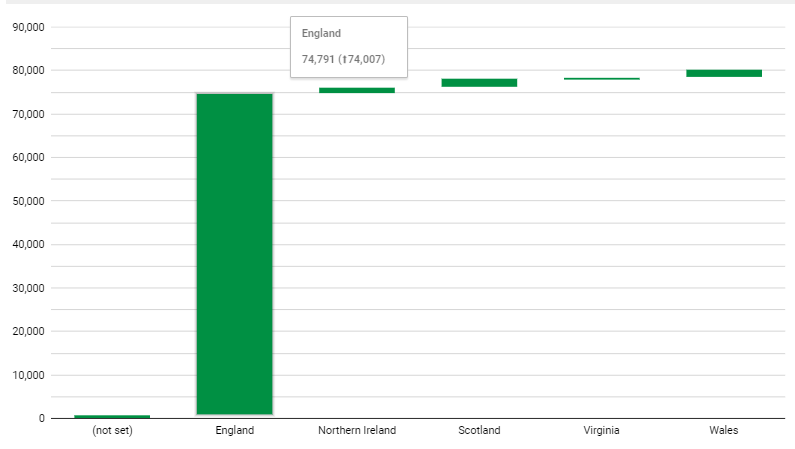
For Example: Consider a company analyzing its annual budget. The waterfall chart would showcase the starting budget, followed by increments for revenue and decrements for expenses, ultimately revealing the net budget at the end.
Tips and Tricks for Waterfall Charts:
1. Color Contrasts: Use distinct colors for positive and negative values to enhance differentiation.
2. Data Labels: Incorporate data labels to provide specific values at each step, aiding in precise interpretation.
3. Total Representation: Highlight the final total to emphasize the cumulative impact of all contributing factors.
4. Axis Scaling: Align the y-axis with data values to prevent distortion and maintain accuracy.
5. Annotations: Integrate annotations to explain specific points or changes within the waterfall structure.